Camera Link
What is Camera Link?
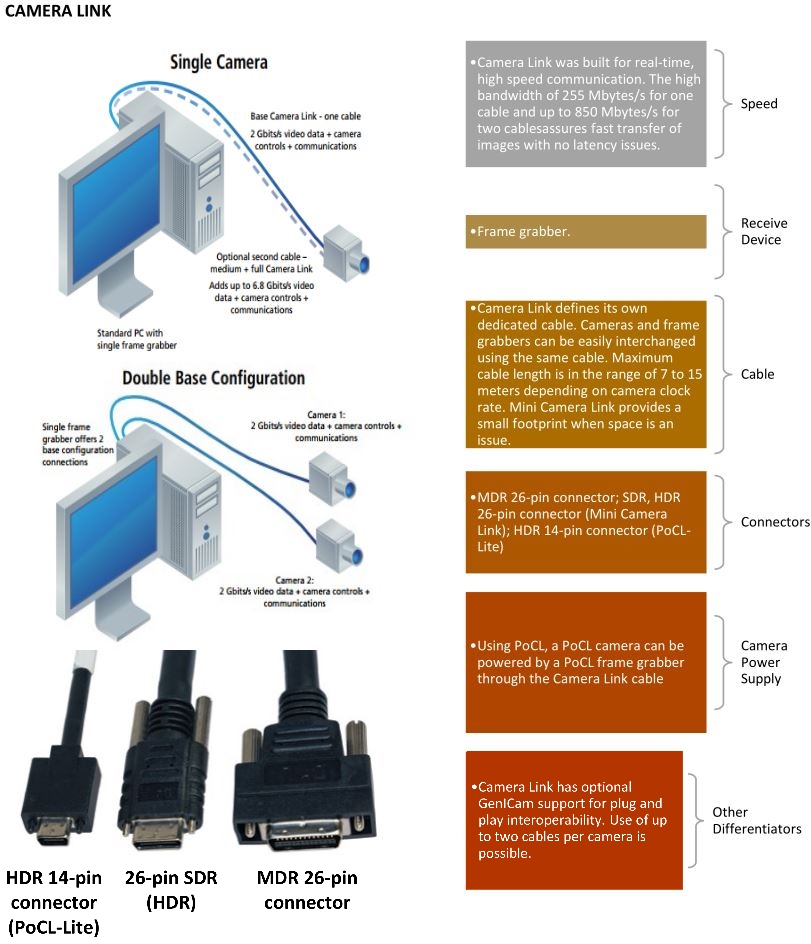
Camera Link is the first universal interface for machine vision.
First released in the year 2000, Camera Link is the culmination of work from companies like Basler, DALSA, EPIX and others with the Automated Imaging Association (AIA). Camera Link supports Direct Memory Access (DMA), bypassing the CPU and freeing system resources. Camera Link also separated control signals from data, allowing lower latencies in imaging acquisition. Camera Link supports up to 680MB/s of data transfer. The high bandwidth allows higher resolution sensors, higher frame rate and high bit-depth images. Camera Link utilizes a frame grabber to get images into the PC via DMA. Frame grabbers can also buffer images, with some high-end frame grabbers even offering some hardware image processing capabilities, further offloading the amount of processing and potentially speeding up the application. Despite the release of Camera Link High Speed (Camera Link HS or CLHS), Camera Link remains a popular choice for real time processing and high bandwidth. Camera Link is currently in its second generation (CLHS is NOT Camera Link 2).
Camera Link comes in three standard configurations: Base, Medium, and Full.
Base allows a data throughput of 255 MB/s
Medium adds a second cable and has a data throughput of 510 MB/s
Full also uses a second cable and uses 680 MB/s
Camera Link has the option of delivering power via Power over Camera Link (PoCL).
All Camera Link cameras and framegrabbers will have a female receptacle. To connect, simply use a Male-to-Male Camera Link Cable.
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
Like many high-speed digital interfaces, Camera Link utilizes Low Voltage Differential Signals to transmit data.
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
Data is transmitted as Most Significant Bit first, and is latched midway through the high phase of the clock cycle.
Image courtesy of Wikipedia